
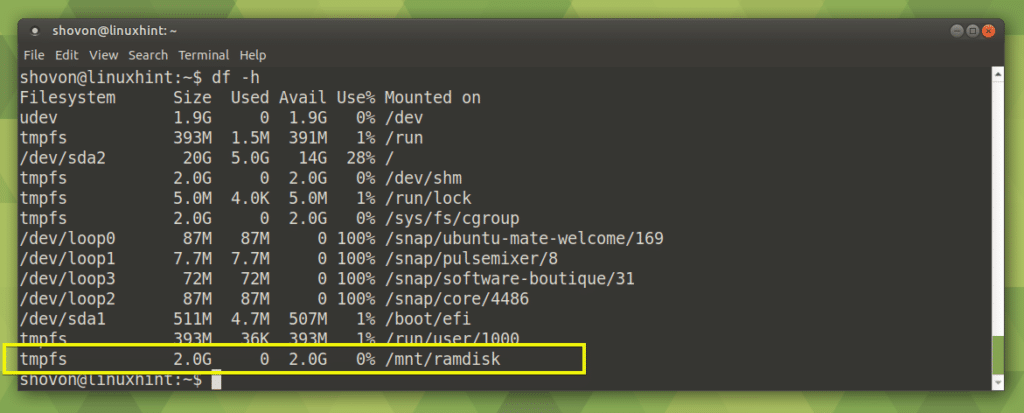
- #Make ram disk sgi linux full
- #Make ram disk sgi linux software
- #Make ram disk sgi linux free
A swap space allows for the kernel to move memory pages that are not likely to be accessed soon to disk (swap or page-out), which will free memory in RAM for the current task. The purpose of the space is to provide disk storage to the kernel when internal memory (RAM) is under pressure. There is no perfect value for swap space size.

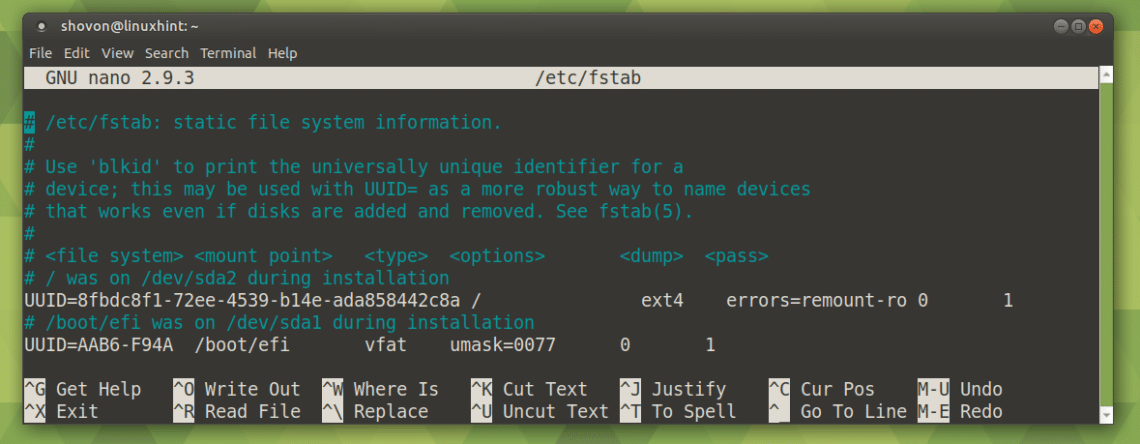
Installations that intend to use systemd as the service and init system must have the /usr directory available at boot, either as part of the root filesystem or mounted via an initramfs.
There is also a 15-partition limit for SCSI and SATA unless the disk uses GPT labels. Since the generation and maintenance of an initramfs is beyond the scope of this handbook, we recommend that newcomers do not use a separate partition for /usr/. A separate partition for /usr/ may require the administrator to boot with an initramfs to mount the partition before other boot scripts start. If not configured properly, the system might have lots of free space on one partition and little free space on another. However, multiple partitions have certain disadvantages as well: Security can be enhanced by mounting some partitions or volumes read-only, nosuid (setuid bits are ignored), noexec (executable bits are ignored), etc. If necessary, file system checks are reduced in time, as multiple checks can be done in parallel (although this advantage is realized more with multiple disks than it is with multiple partitions). The entire system cannot run out of free space if one defunct tool is continuously writing files to a partition or volume. Choose the best performing filesystem for each partition or volume. Separate partitions or volumes have the following advantages: How many partitions and how big very much depends on considering the trade-offs and choosing the best option for the circumstance. This space estimate excludes the /var/cache/distfiles and /var/cache/binpkgs directories, which will gradually fill with source files and (optionally) binary packages respectively as they are added to the system. By default, /var hosts the Gentoo ebuild repository (located at /var/db/repos/gentoo) which, depending on the file system, generally consumes around 650 MiB of disk space. usr hosts the majority of applications available on the system and the Linux kernel sources (under /usr/src). In most situations on Gentoo, /usr and /var should be kept relatively large in size. The reason for these recommendations is similar to the /home directory: security, backups, and maintenance. #Make ram disk sgi linux software
Game servers may have a separate /opt partition since most gaming server software is installed therein. If Gentoo is being installed to perform as a mail server, then /var should be a separate partition as all mails are stored inside the /var directory. If there are lots of users, then it is advised to have /home on a separate partition which will increase security and make backups and other types of maintenance easier. The design of disk partition layout is highly dependent on the demands of the system and the file system(s) applied to the device. These are called partitions.ĭesigning a partition scheme How many partitions and how big?
#Make ram disk sgi linux full
Instead, full disk block devices are split up in smaller, more manageable block devices. 3.1 SGI machines: Creating an SGI disk labelĪlthough it is theoretically possible to use a full disk to house your Linux system, this is almost never done in practice.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
